

"Biomimetic Pearl system allows this type of clinical case to be treated quickly, with a lower surgical risk and fewer post-operative complications, allowing the patient to recover a certain level of function on the same day as the surgery. Current good behaviour of the mini-implants, of a diameter of less than 3 mm, which allows them to be used clinically to fix removable dentures with stability in the long term."
Introduction
Treatment with reduced-diameter implants is especially indicated in patients when conservative surgery is desirable because complex surgery is contraindicated1. Another type of indication would be in the oral rehabilitation of completely toothless patients and in advanced atrophies of the maxilla and mandible2.
Current clinical evidence advises the use of reduced-diameter implants in the mandible with both conventional and immediate loading protocols3. In the latter case, the main surgical recommendations for the treatment to be predictable are4:
Clinical Case
Patient aged 78, with controlled high blood pressure, controlled diabetes mellitus, complete arrhythmia due to auricular fibrillation treated with Simtrom, is referred to our centre by another clinic because she wants to try to “fix” the complete bottom dentures. The patiently currently only puts them in to leave the house.
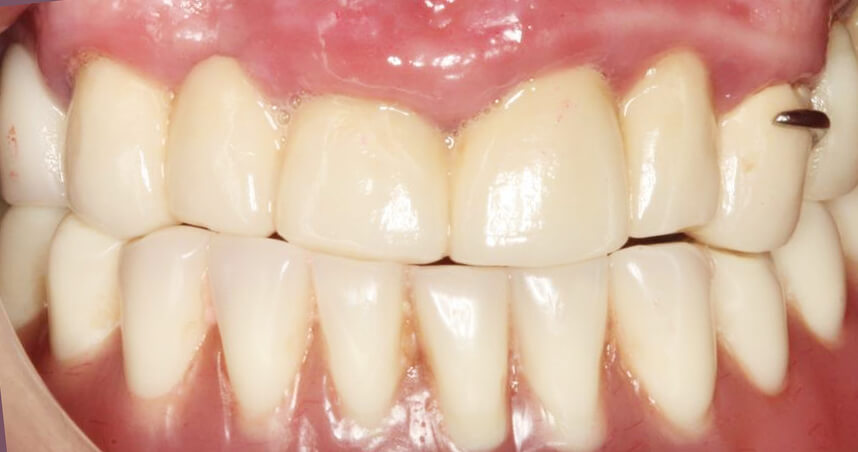 Image 1 – Current dentures of the patient
Image 1 – Current dentures of the patient
In the initial image, it is possible to observe the complete bottom dentures, which are two years old, and a metal-ceramic top bridge from 14 to 23, with a metal unmovable partial prosthesis. In the clinical examination, we note an elderly lady, very active and cooperative, who speaks very fast and easily removes the whole bottom dentures, because she says that their constant moving makes her nervous. We note conserved residual crests, but on mobilising the muscular edges the neutral space disappears straight away, leaving the floor of the mouth flat at some points and making it difficult for the dentures to stop moving upwards.
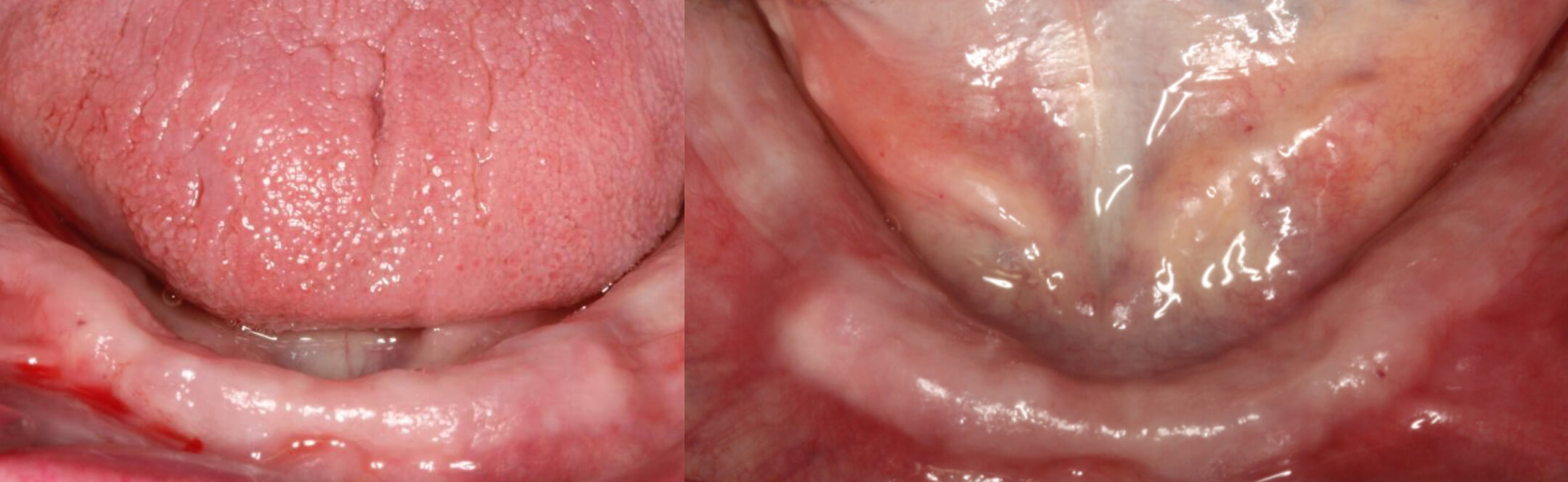 Image 2 and 3 – Initial state of the case
Image 2 and 3 – Initial state of the case
Bearing in mind the base pathology presented by the patient and her financial disposition, it was decided to instal reduced-diameter implants using the transmucosal technique, as the available bone width allowed this type of technique to be carried out safely. To do this, Biomimetic Pearl implants with a 2-mm diameter by 10-mm length were chosen. It was explained to the patient that if the stability of the implants allowed it, it would be attempted to carry out an immediate loading with her previous dentures.
On the day of the surgery, it was verified that her INR was 2.4, peripheral glycaemia was 120 mg/100 ml and 2 gr of Amoxicillin were administered prior to the intervention. The procedure was initiated by anaesthetising the patient with Articaine 4% with 1:200.00 of epinephrine. The round scalpel was used to mark the insertion points of the implants and the mucus plug was eliminated. The milling sequence was initiated in the anterior sector with a 1.3m mill and, as the bone was type II, the milling depth was to 6mm. In the posterior sector, because the bone appeared to be a slightly softer type III, the 1.3 mm diameter mill was changed for an 8 mm one. The four implants were put in place achieving primary stability in all of them with torques between 35 and 45 Ncm.
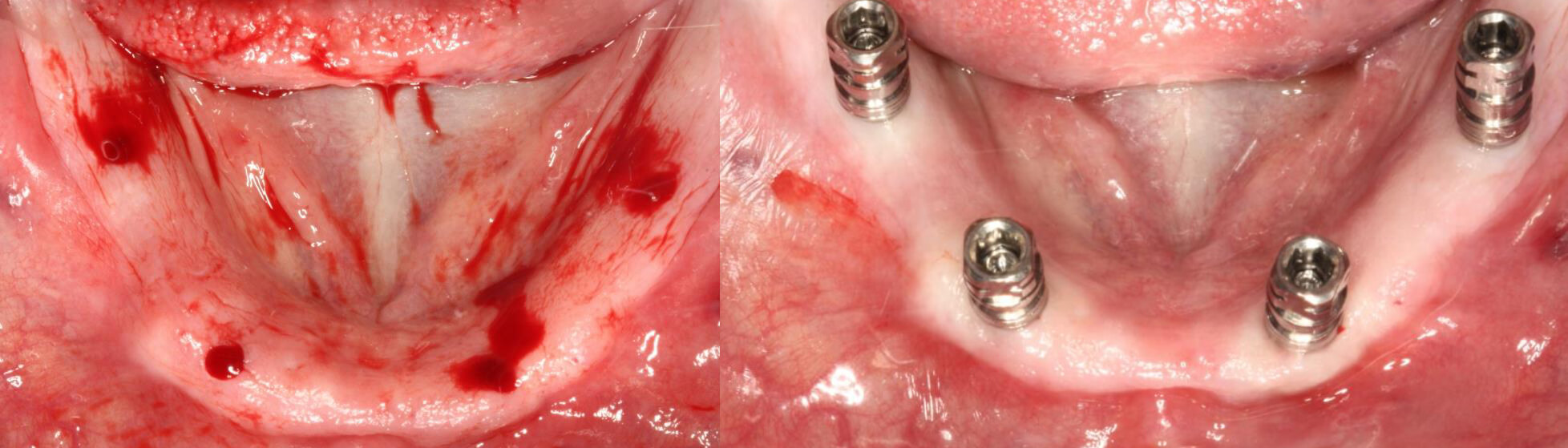 Image 5 and 6 – Close-up of the milling | View of the implants in place
Image 5 and 6 – Close-up of the milling | View of the implants in place
Given the good stability of all implants, it was decided to carry out an immediate loading with the provisional dentures.
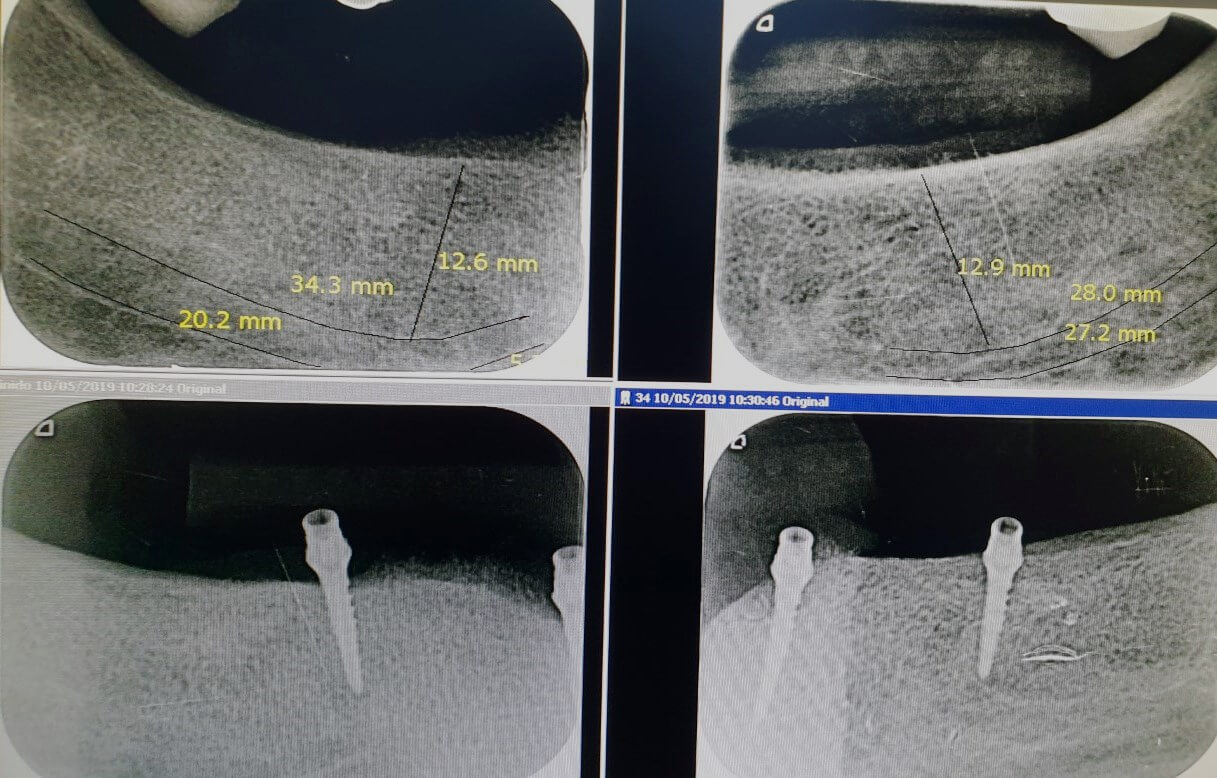 Image 7 – X-ray of the implants in place
Image 7 – X-ray of the implants in place
On account of the small quantity of epithelium of the patient, it was decided to screw in Rhein abutments with a height of 0.8 mm. The novel design of the Pearl implants system allows the abutments to be introduced through the implant transporter, avoiding collapse of the gums and offering the patient maximum comfort.
 Image 8 – Different heights of the Rhein abutments for overdentures
Image 8 – Different heights of the Rhein abutments for overdentures
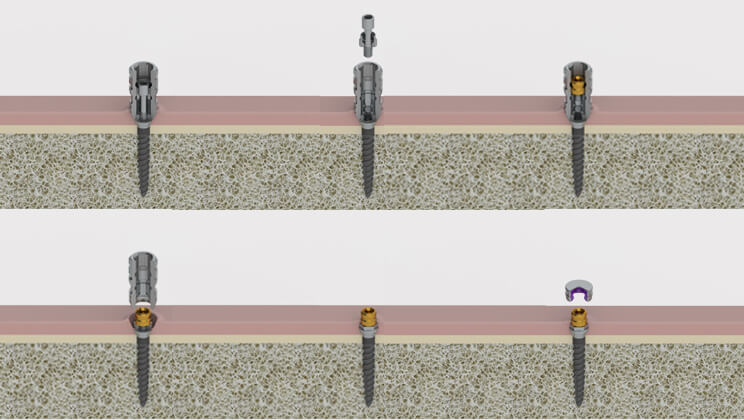 Image 9 – Close-up of the installation of the abutments through the implant’s transporter
Image 9 – Close-up of the installation of the abutments through the implant’s transporter
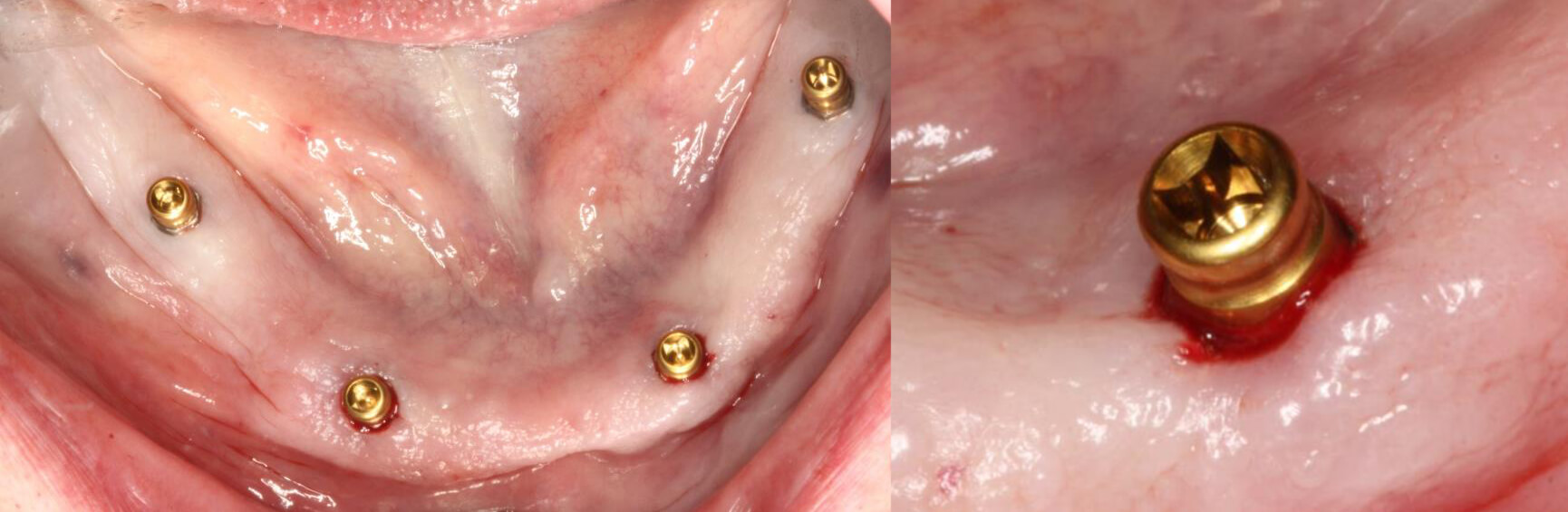 Image 10 and 11 – Abutments for overdentures post-surgery
Image 10 and 11 – Abutments for overdentures post-surgery
Once the abutments were screwed to the implants, the impressions were taken for manufacture of the provisional dentures on the basis of the patient’s complete rehabilitation. To do this, metal copings were put in place with the Teflons on the Rhein abutments and the impression was taken by overcoating the dentures with resin.
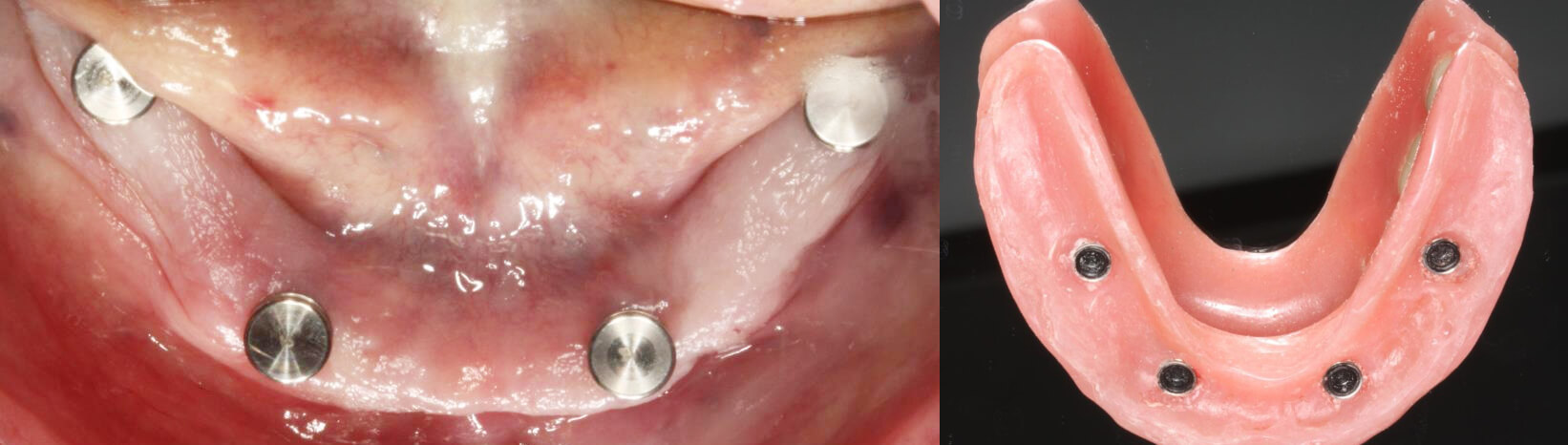 Image 12 and 13 – Preparation for the impression / View of the provisional dentures with the attachments inserted
Image 12 and 13 – Preparation for the impression / View of the provisional dentures with the attachments inserted
The patient was instructed to keep the dentures in place for one month without removing them. She was also instructed to use a 0.12% Chlorhexidine mouthwash during one minute every 12 hours, and was recommended a soft diet. After this time, the dentures were removed, verifying that the implants were stable and noting slightly hyperaemic tissues. At this moment, the Teflons were replaced with yellow-coloured (0.6 kgf) Teflons with gentler retention.
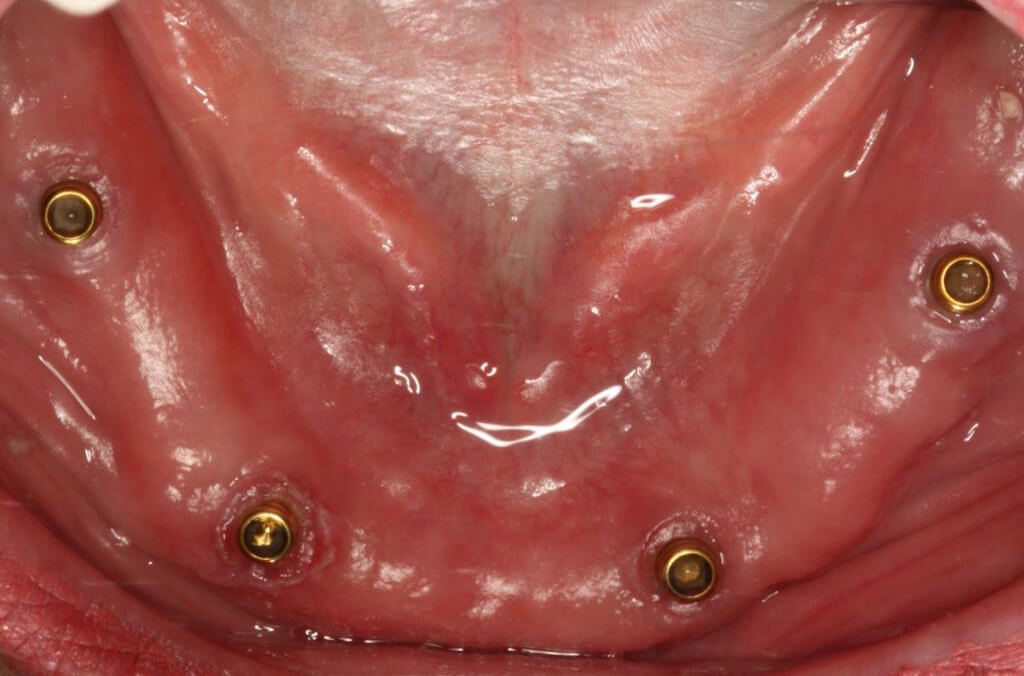 Image 14 – Tissues one month after implant placement
Image 14 – Tissues one month after implant placement
Finally, it was decided to keep the patient with the same denture during three months for subsequent preparation of the definitive overdenture with a metal internal structure.
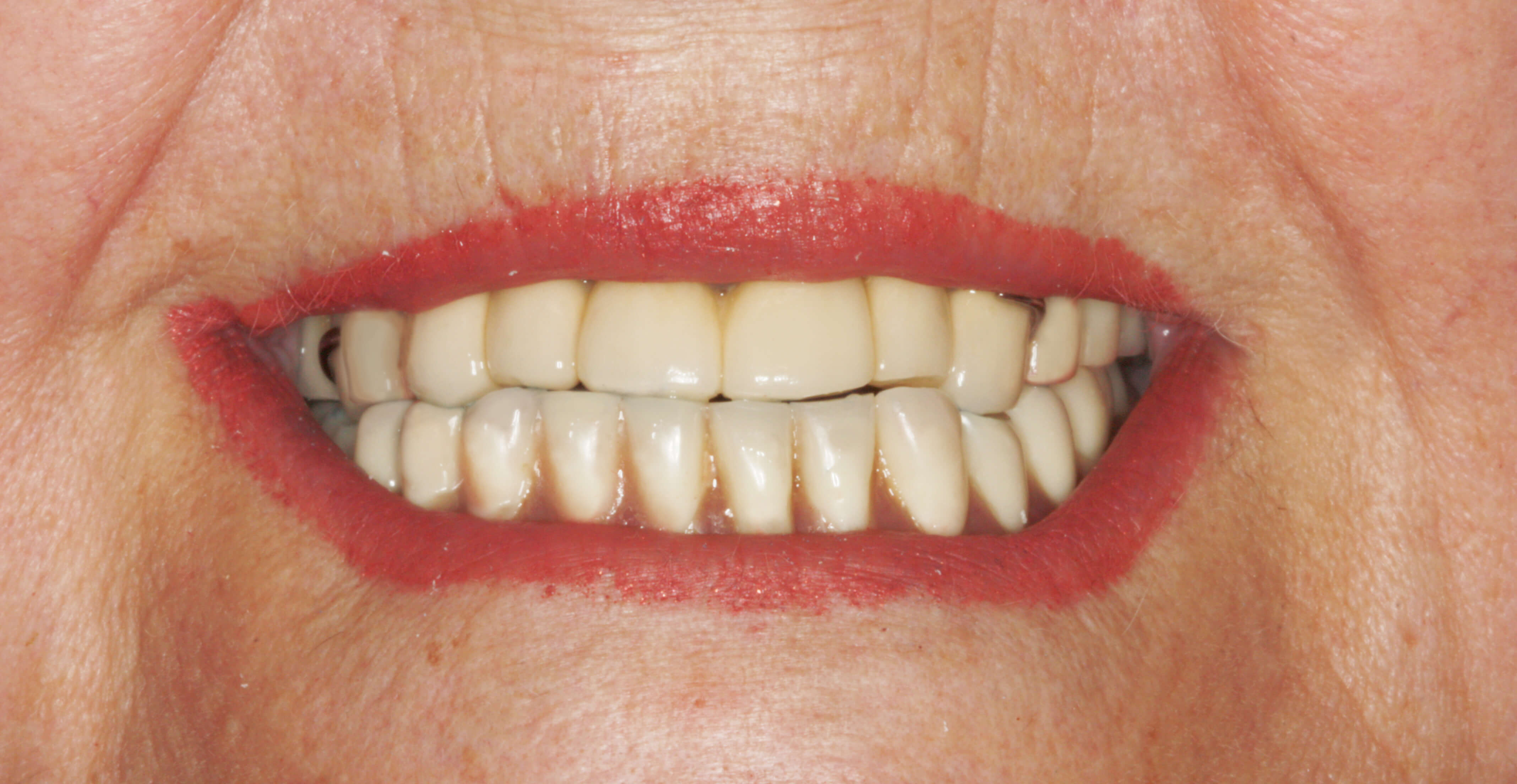 Imagen 15 – Final result
Imagen 15 – Final result
Conclusion
Biomimetic Pearl system allows this type of clinical case to be treated quickly, with a lower surgical risk and fewer post-operative complications, allowing the patient to recover a certain level of function on the same day as the surgery. Current good behaviour of the mini-implants, of a diameter of less than 3 mm, which allows them to be used clinically to fix removable dentures with stability in the long term.
References