

Among the types of prostheses available today, hybrids are an implant restoration option that can help patients have a fixed denture and restore their oral function, as well as offering an acceptable esthetic at a reasonable price.
Among the types of prostheses available today, hybrids are an implant restoration option that can help patients have a fixed denture and restore their oral function, as well as offering an acceptable esthetic at a reasonable price.
The solution primarily comprises a metallic structure screwed to a specific number of dental implants, depending on whether the upper or lower arch is to be restored, and this is coated by an acrylic material into which artificial resin teeth are anchored of the color, size and angle that match the patient’s orofacial features.
One of the main advantages of this type of prosthesis is that patients feel comfortable wearing a fixed structure, providing them with good proprioception to improve their quality of life. At the same time, it is easy for specialist dentists to maintain and repair the acrylic resin and teeth when required, as is often the case due to the weak retention of the materials used.
But one possible disadvantage as regards other types of restorations may be the natural look of the final esthetic result, which perhaps does not fully satisfy patients.
Presenting this clinical case allows us to show the remarkable evolution of this type of restoration. An innovative system of fixed titanium structures conceived and designed in various architectures to be used with different prosthetic restoration materials and methods, thereby helping to improve the work of professionals.
Presentation of clinical case
We received a 73-year-old, non-smoking male patient at the clinic with no significant medical history.
His main concern was the impossibility of chewing food because of the absence of teeth in posterior regions and fracture of anterior teeth.
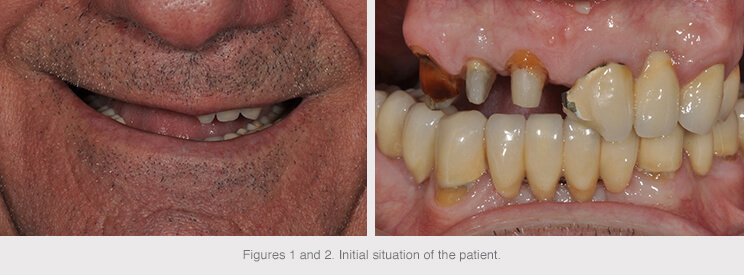
Removal of the upper teeth was suggested because of the presence of tooth stumps with secondary caries and absence of the ferrule required for their reconstruction.
We proceeded to extract all the remaining upper teeth and curetted the periapical lesions. An immediate full prosthesis was positioned in the patient for three months to allow the tissues to heal properly.
After this time, six (Avinent) Biomimetic Ocean IC implants of the following sizes were positioned: three 4 x 15 mm implants in positions 26, 24 and 12; two 3.5 x 15 mm implants in positions 22 and 14, and finally a 4 x 13 mm implant in position 16.
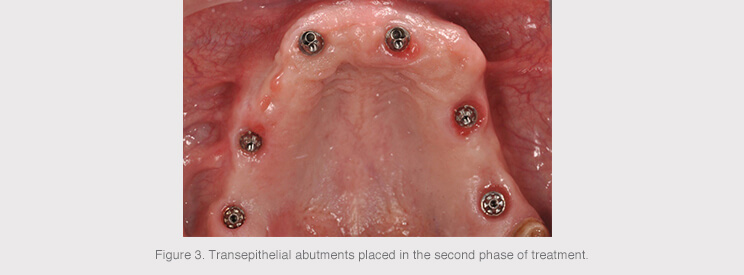
The decision was made to wait four months from the positioning of the implants before conducting the second surgical phase, in which 17-degree angled transepithelial abutments were positioned in 12 and 22 and straight abutments in the remaining implants, all from Avinent.
It was thought appropriate to use a less rigid material in the upper full prosthesis because the patient had a lower fixed ceramic prosthesis, thereby reducing the risk of it fracturing and at the same time minimizing the implant transmitted loads.
A digital impression was taken with a Trios Intraoral Scanner (3Shape) to proceed to the design and production of a fixed titanium prosthesis with milled PMMA coating.
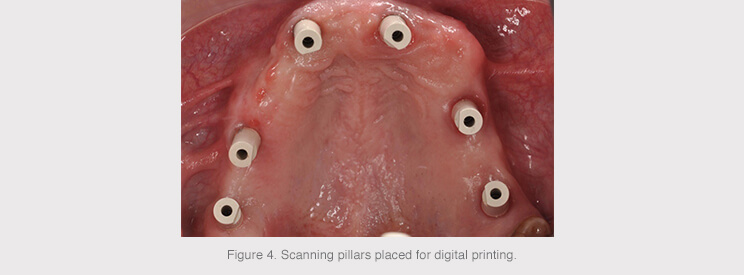
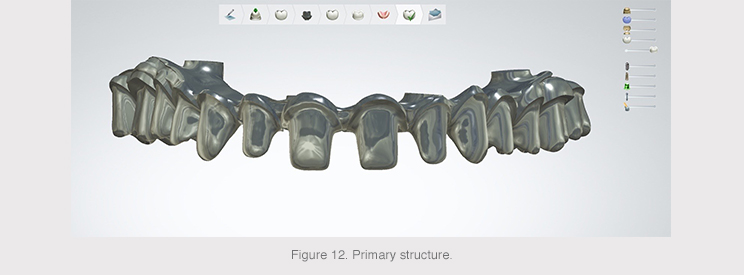
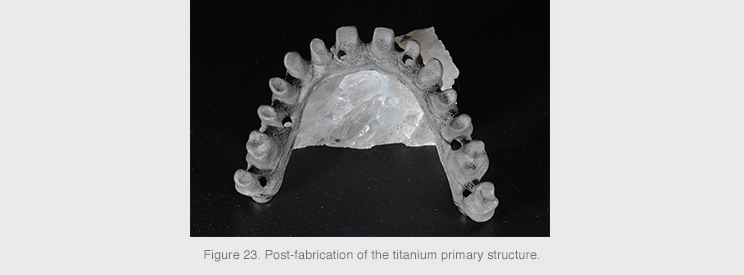
The primary structure comprised a bar printed in titanium grade V, a biocompatible material with optimal biological performance for the proper formation of soft tissue, as well as providing optimal resistance and perfect lightness for these types of complex restorations.
The technology used to produce the primary bar was 3D titanium impression, which helps to obtain any geometry and personalize its surface structure to facilitate many aspects of the dental technician’s work, including resin or composite loading and/or positioning of acrylic teeth.
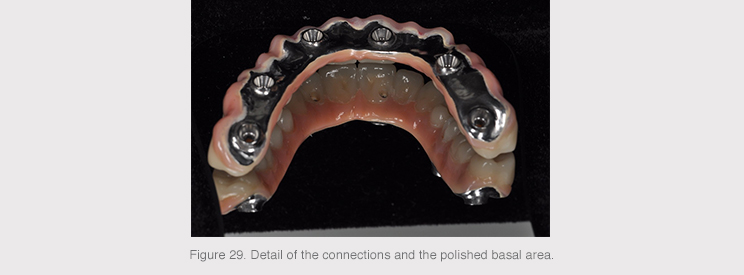
The added value of this titanium structure is the machining of implant connections with HSM milling and the complete polished finish of the basal area that will come into contact with the soft tissue.
Design and production of prosthesis
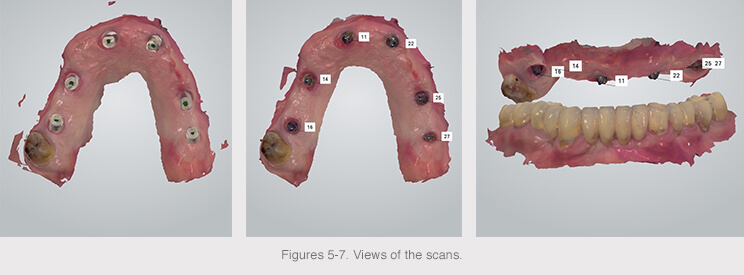
The digital impression was sent to the laboratory to design the final prosthesis with (3Shape) dental design software.
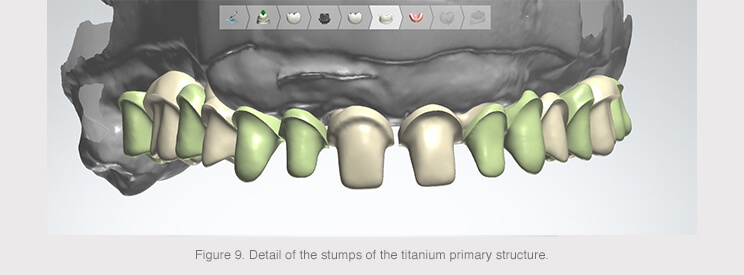
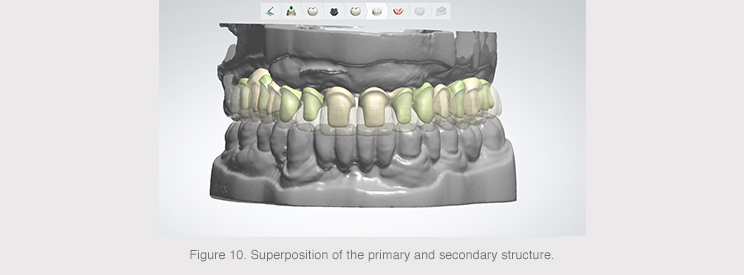
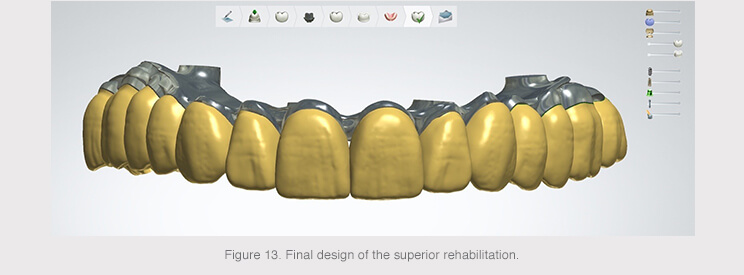
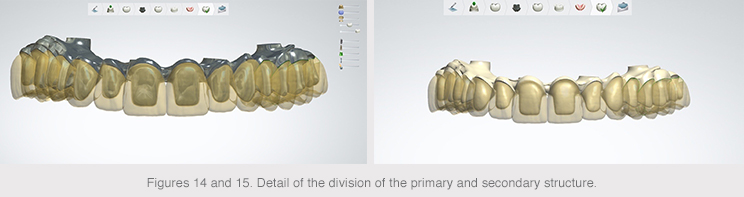
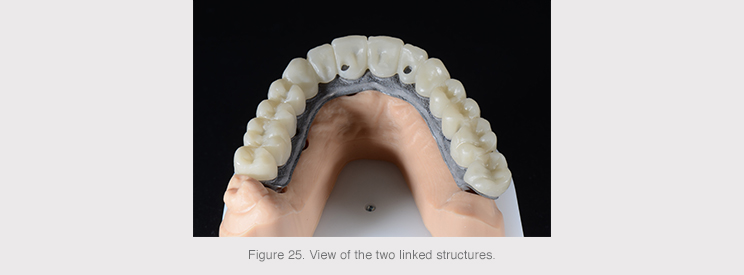
An anatomical reduction was made from the anatomy created from the complete prosthesis in order to obtain two structures: a primary structure made of titanium and a secondary structure made of a less rigid material.
The titanium structure would be screwed into the six implants and the design of the tooth stumps with shoulders facilitated the proper connection of the secondary structure.
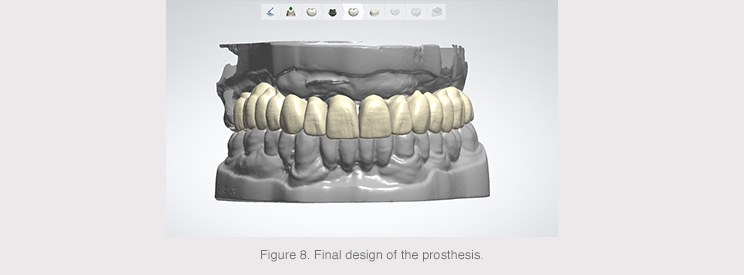
The gum was positioned to complete the primary structure once the final anatomy had been designed.
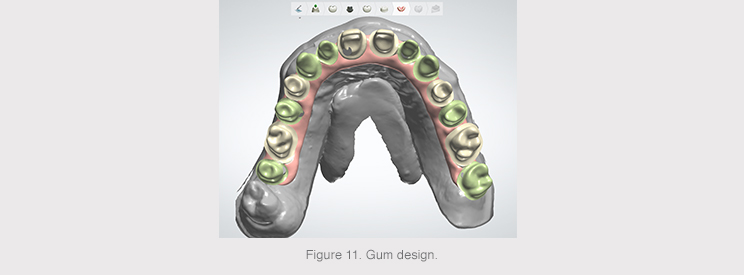
The final designed anatomy was recovered, as well as the same reduced anatomy, in order to separate them into two STL files that were sent to the Avinent-Core3D milling center to mill the two structures.
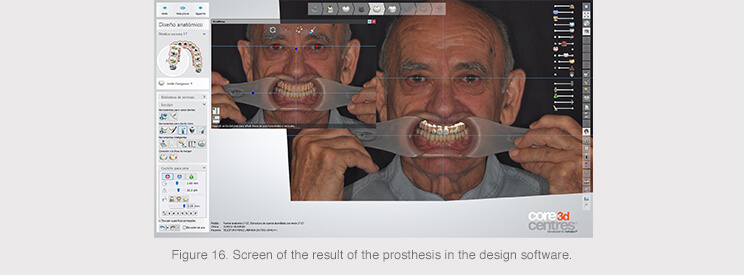
A 3D tooth test was printed once the design of the structure had been validated in order to assess the esthetic and occlusion of the final restoration in the patient’s mouth.
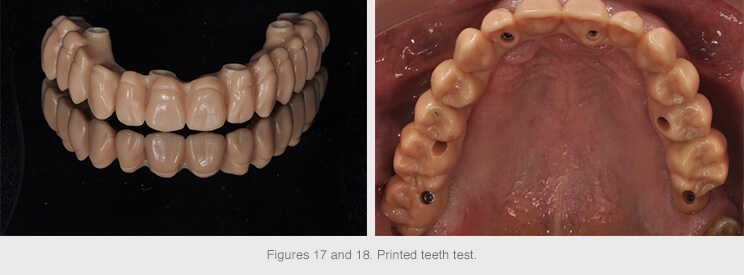
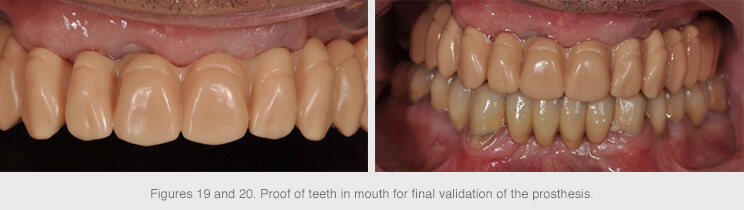
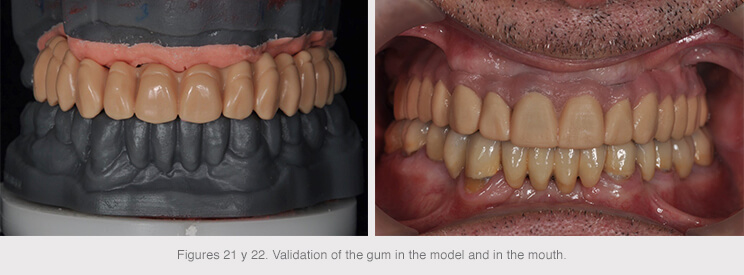
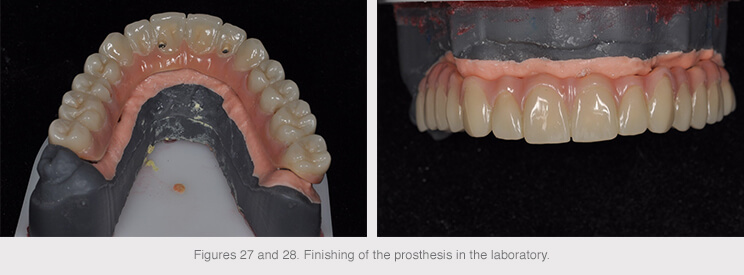
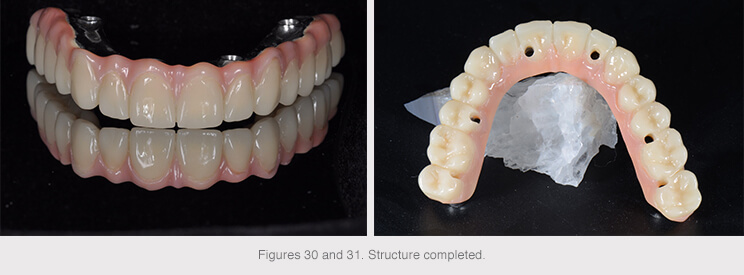
The structures were then produced following validation.
3D titanium impression was used for the base structure and HSM milling for the implant connections. This production method provides an ideal surface roughness for the retention of coating materials that are to be subsequently applied in the dental laboratory.
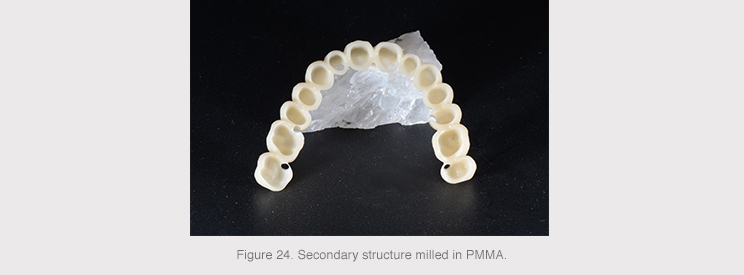
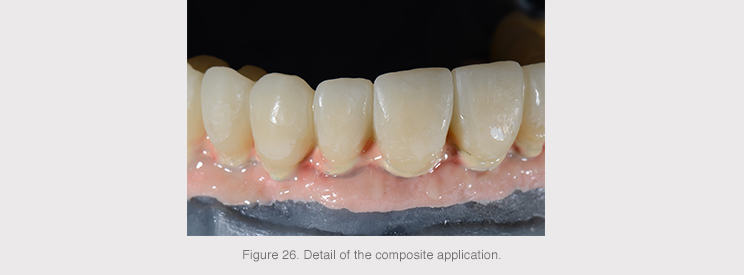
The secondary structure was milled in PMMA, a translucent, strong, easy-to-mold polymeric material that was composite bonded to the primary titanium structure to obtain the final prosthesis.
The sector is progressing towards new, more efficient, natural and patient-friendly restorations that also meet the esthetic and functional challenges of dentistry 4.0.
By using the experience it has acquired in 3D printing and CAD/CAM technology, Avinent has developed some innovative laboratory designed structures to facilitate and expand the range of complex fixed restorations found on the market today.
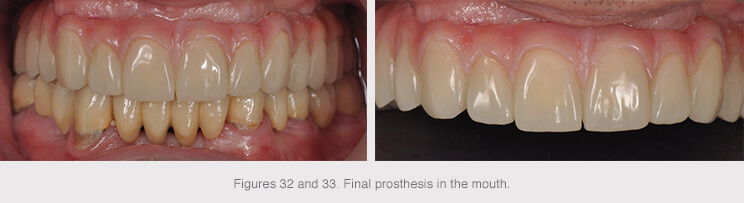
New designs and materials provide reduced rigidity and better retention of resins and/or composites, thereby helping make the structures feel more comfortable in the patient’s mouth. In addition to the ease and shorter handling time in the event of having to repair them.
These new materials have also greatly improved when it come to the degree of finish, helping us to obtain esthetically satisfying results and proper soft tissue maintenance.